-ERC GeoWAT

Introduction
Over the next five years, GEOWAT will try to find an answer to the seemingly simple but often avoided question: How much groundwater is there, and how long will it last?
We need groundwater for, among other things, our water and food supply. Across the globe, however, groundwater reserves are being depleted due to explosive population growth and economic development.
“With this grant we can really make a giant leap (see the figure below) in understanding the problem of worldwide groundwater depletion. It allows us to globally map the volumes of extractable fresh groundwater resources and define ecologically and economically sustainable pathways of future groundwater development.”
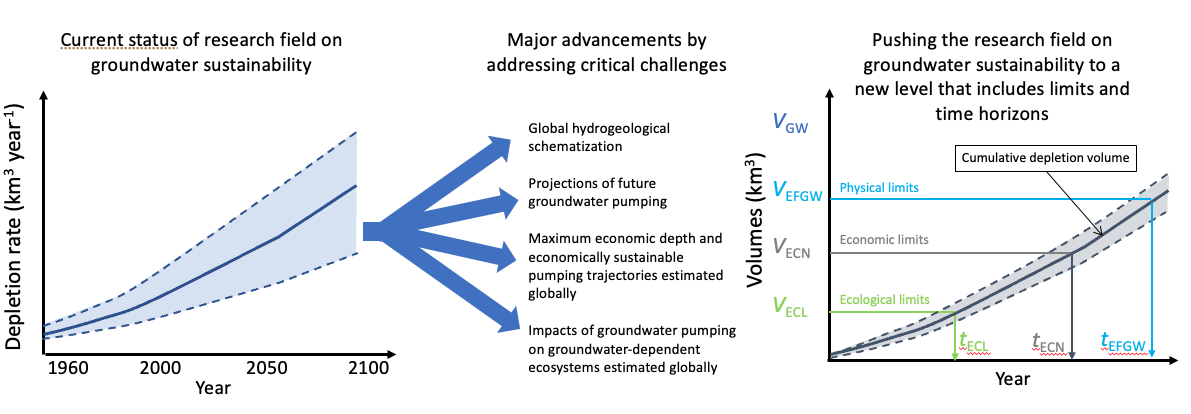
Pushing the field of global groundwater sustainability from a situation of various estimates of very different depletion rates, to one where the physical, economic, and ecological limits of global groundwater are truly quantified in terms of extractable volumes and time horizons; VGW: total groundwater volume; VEFGW: (physically) extractable fresh groundwater volume; VECN: volume groundwater that can be exploited economically; VECL: volume groundwater that can be withdrawn without undesirable harm to ecosystems; tEFGW, tECN etc. are the associated time horizons of depleting these volumes; volumes, times and associated pumping depths will be assessed globally at 30 arc-second (~ 1 km) resolution; the shaded areas between dashed lines represent uncertainty bounds.
Objective and research questions
With the GEOWAT project, we will address these open research challenges with the aim to spatially determine how much groundwater there is and how long will it last. GEOWAT will achieve this by globally assessing the limits of groundwater use in three key objectives (KO):
- Determine the physical limits of groundwater use by estimating the volume of total and fresh groundwater, estimating how much of that volume is physically extractable, and projecting the time to physical depletion of groundwater reserves under future climate and socioeconomic scenarios.
- Determine the economic limits of groundwater use by estimating the maximum depth at which groundwater withdrawal is still profitable under current land use and future scenarios, and by finding withdrawal trajectories that are economically sustainable over time.
- Determine the ecological limits of groundwater use by estimating how groundwater withdrawal affects groundwater-dependent ecosystems globally and valuating resulting ecosystem deterioration economically.
Research design
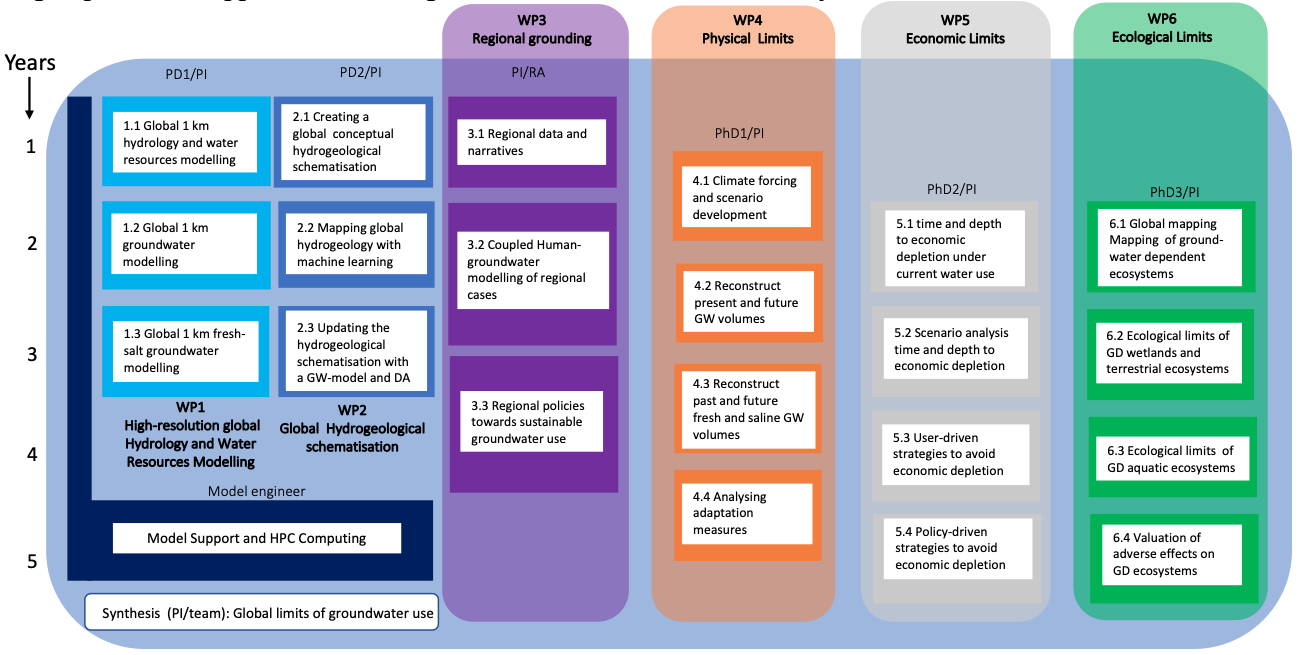
Research design: division into work packages and tasks over the 5 years. WP1 and WP2 develop the model infrastructure (physically-based global-scale surface water-groundwater model; GLAM) used in the global analyses of WP4-6. Regional case studies in WP3 serve as additional validation of global results and to evaluate/add regional relevance to the global assessments in WP4-6. Support by a model engineer is available for all WPs. Uncertainty assessment is integral: results will be reported in terms of mean values and uncertainty measures.
Synergy with NGS World water Map
Together with National Geographic Society and ESRI, Utrecht University is cooperating in the World Water Map and World Water Map: Insights. Here the global water gap is estimated for the past and projected for the future and disseminated the general public, data journalists and policy makers. Synergy with GEOWAT occurs through global hydrological modelling (WP1; Bram Droppers) and the regional grounding in water scarcity hotspots (WP3; Myrthe Leijnse)
Personnel
The following people contribute to GEOWAT
Prof. Marc F.P. Bierkens – PI of GEOWAT; involved in all work packages
Dr. Edwin H. Sutanudjaja (WP1)- Scientific model engineer: developing of PCR-GLOBWB and improving model performance (GLAM)
Dr. Kor de Jong (WP1) – Research software engineer; improving parallelisatio
Dr. Jarno Verkaik (WP1; now at Deltares) – global hyper-resolution global groundwater modelling
Dr. Bram Droppers (WP1) – Scientific model engineer (supported by National Geographic Society): AI-based surrogate modelling to speed up calculations and calibrate PCR-GLOBWB
Dr. Daniel Zamrksy (WP2) – postdoc: Global hydrogeological schematisation (HYGS)
Myrthe Leijnse, MSc (WP3) – PhD student (supported by National Geographic Society): Hotspots of water scarcity
Barry van Jaarsveld, MSc (WP4) – PhD student: Physical limits to global groundwater use
Sioux F. Melo Leon, MSc (WP5) – PhD student: Economic limits to global groundwater use
Sneha Chevuru, MSc (partly supported by EU AquaConnect): Global crop growth modelling
Nicole G. Otoo, MSc (WP6)-PhD student: Ecological limits to global groundwater use
Apart from the PI PhDs are supervised by both internal and external supervisors: Myrthe (dr. Niko Wanders); Barry (dr. Niko Wanders); Sioux (dr. Rens van Beek; dr. Stijn Reinhard); Sneha (dr. Rens van Beek, prof. Michelle van Vliet); Nicole (prof. Michelle van Vliet, dr. Edwin Sutanudjaja, dr. Aafke Schipper).
Example outputs from the different WPs
Changes regularly (under construction)
WP1
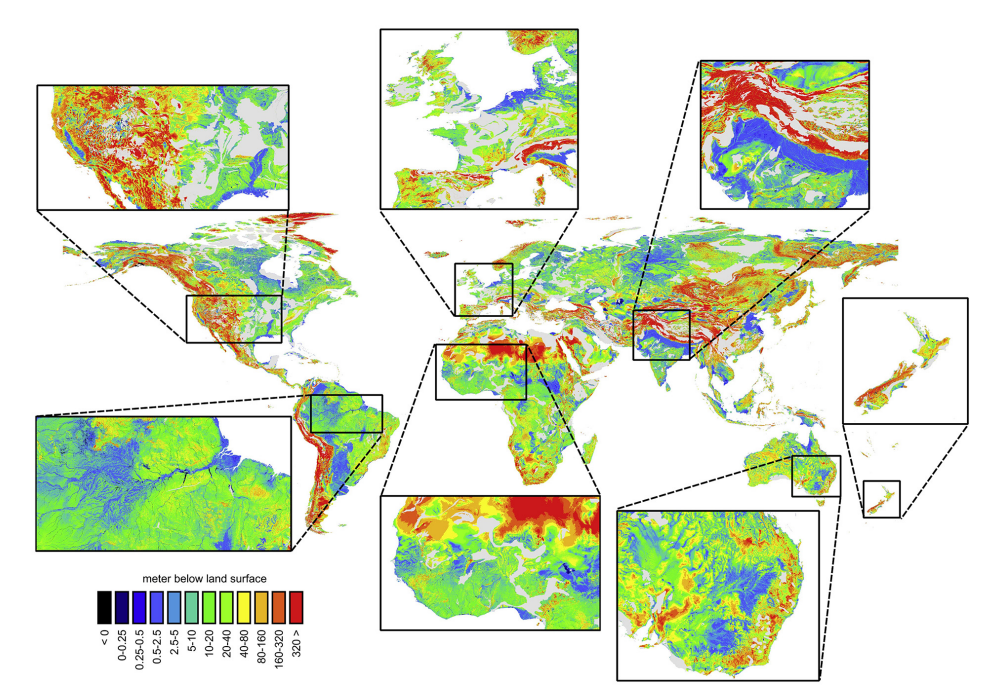
Mean groundwater head from our transient global 1 km groundwater model GLOBGM (Verkaik et al., 2024)
1 km global simulations with PCR-GLOBWB (van Jaarsveld et al., 2024)
WP3
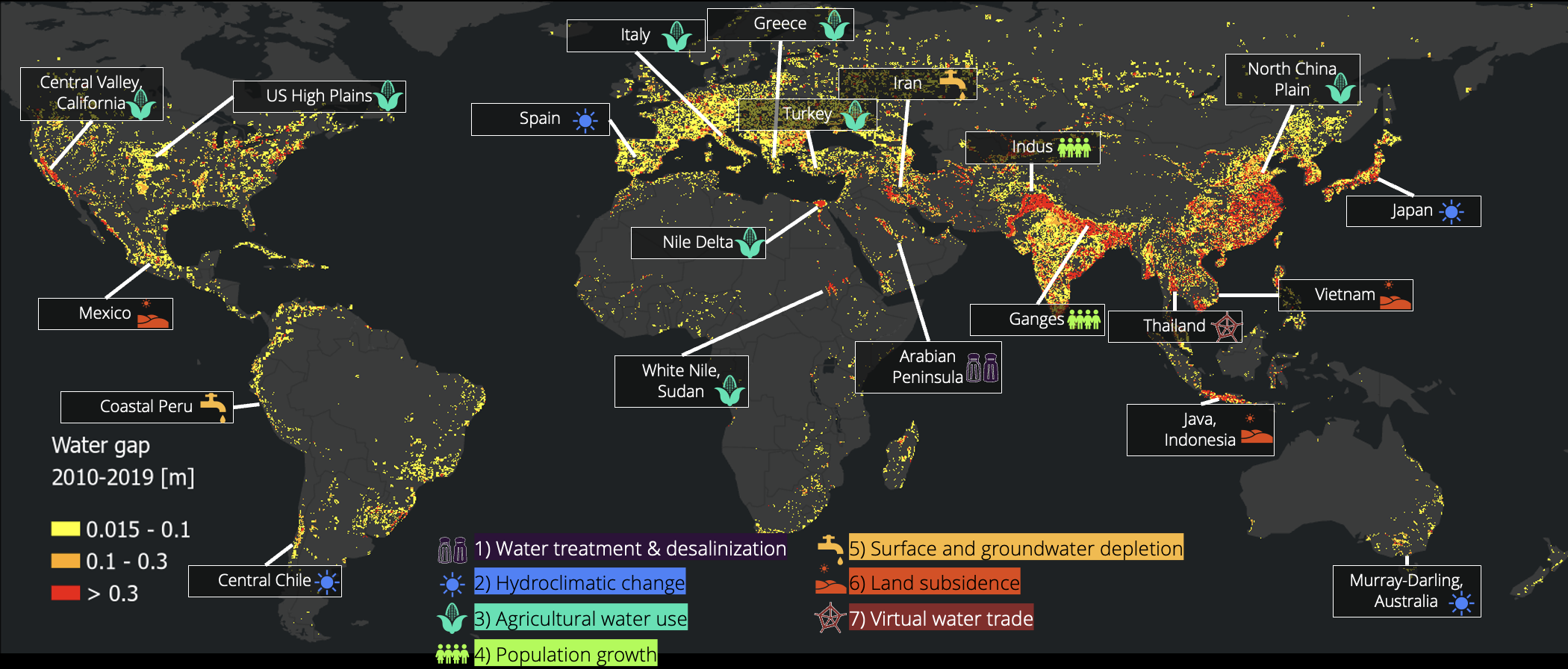
Map with water scarcity hotspots: water gap and drivers of water scarcity (Leijnse et al., 2024)
WP4
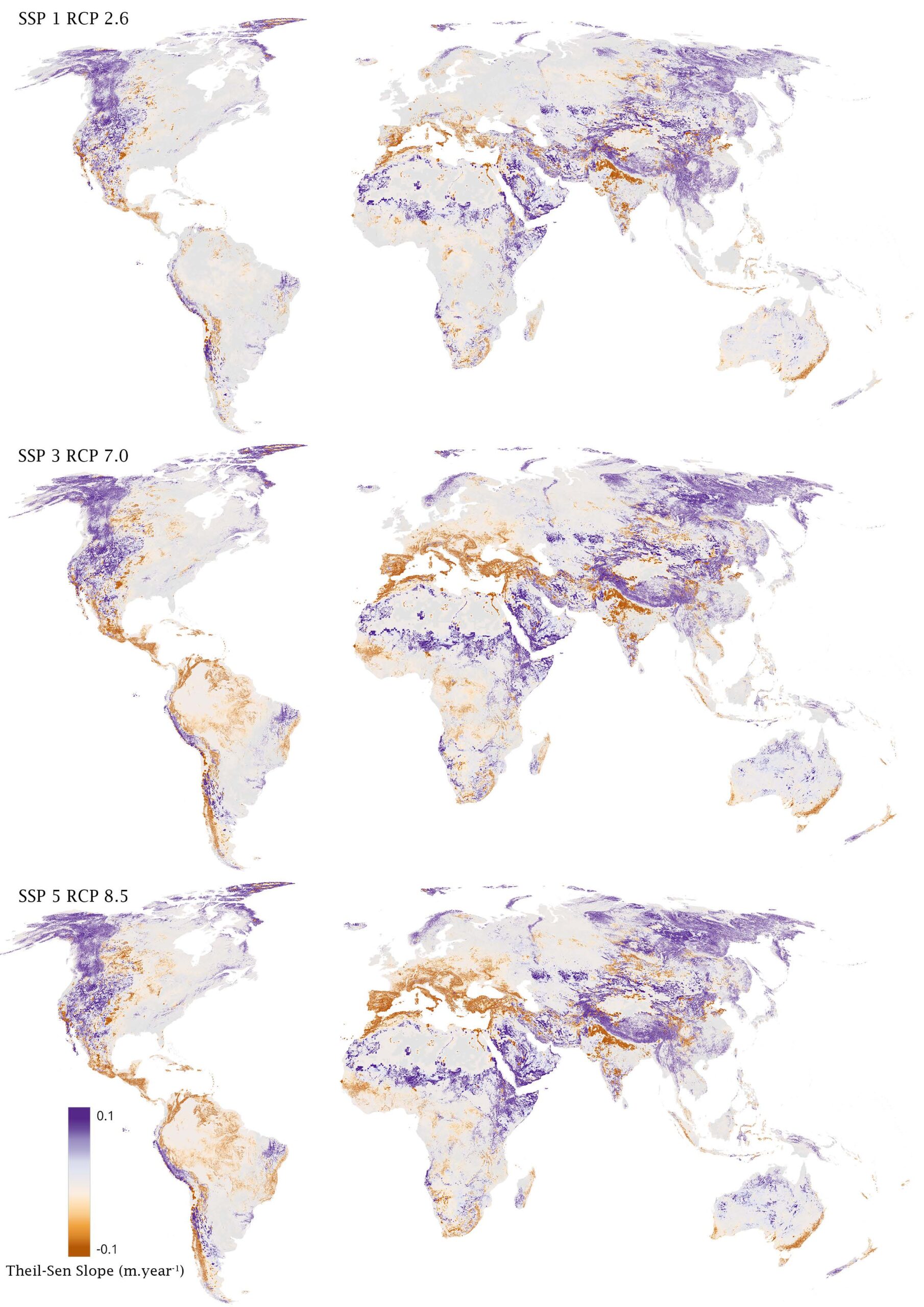
Ensemble mean change of Theil-Sen slopes of changes in groundwater heads as projected by a combination of PCR-GLOBWB recharge and surface water levels and GLOBGM groundwater a 1 km (van Jaarsvel et al., in prep).
WP5
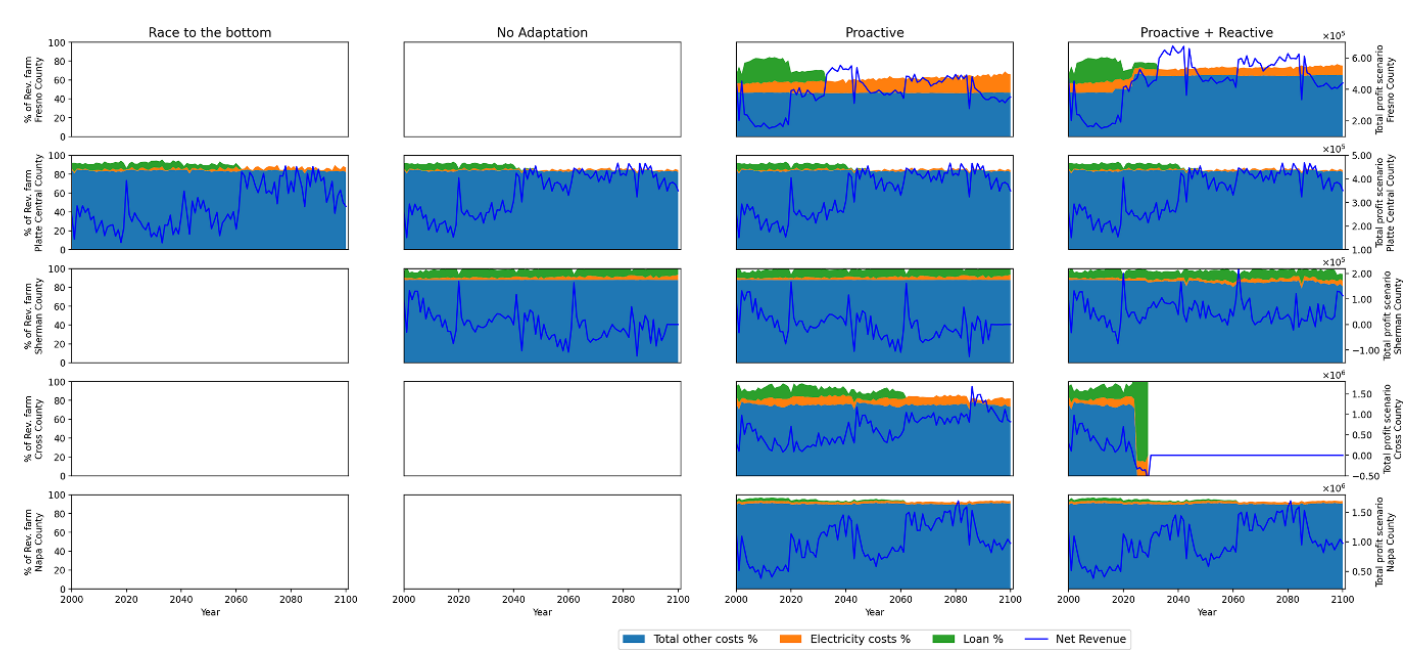
Simulations of cropping costs components (% total: stacked areas) and profits (USD/ha: blue line) over time t under groundwater depletion for several locations across the U.S. using the farms-scale hydroeconomic decision model HELGA (Melo-Leon et al., 2024).
WP6
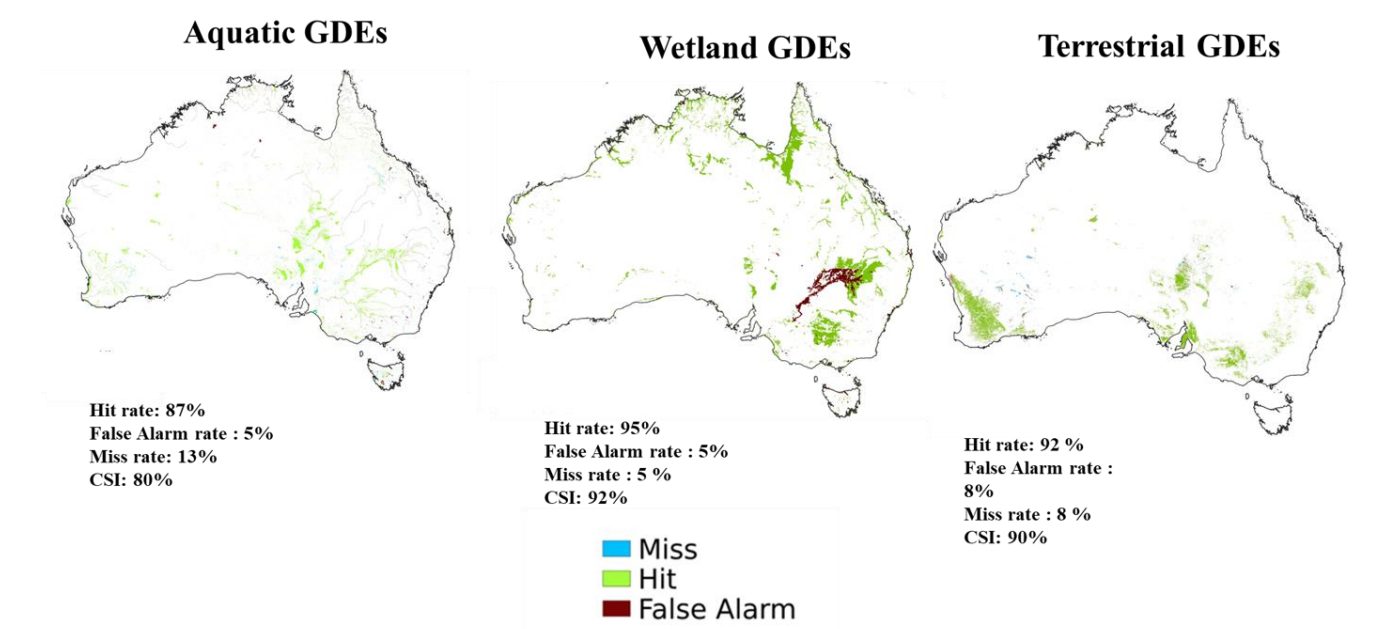
Mapped groundwater dependent ecosystems (GDEs) over Australia based on our 1 km GLOBGM global groundwater model and PCR-GLOBWB. Hit, fall and miss rates are calculated based on the Australian GDE atlas (Otoo et al., 2025).
Publications
2025
Otoo, N. G., Sutanudjaja, E. H., van Vliet, M. T. H., Schipper, A. M., and Bierkens, M. F. P. (2024). Mapping groundwater-dependent ecosystems using a high-resolution global groundwater model. Hydrology and Earth System Science, 29, 2153–2165. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-29-2153-2025.
Zamrsky, D., Ruzzante, S., Compare, K., Kretschmer, D., Zipper, S., Befus, K. M., Reinecke, R., Pasner, Y., Gleeson, T., Jordan, K., Cuthbert, M., Castronova, A. M., Wagener, T., & Bierkens, M. F. P. (2025). Current trends and biases in groundwater modelling using the community-driven groundwater model portal (GroMoPo). Hydrogeology Journal, 33(2), 355-366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-025-02882-7
https://research-portal.uu.nl/ws/files/262148243/s10040-025-02882-7.pdf
Chevuru, S., Lamsal, G., (Rens) van Beek, L. P. H., van Vliet, M. T. H., Marston, L., & Bierkens, M. F. P. (2025). Comparing crop growth models across the contiguous USA with a focus on dry and warm spells. Agricultural Water Management, 311, Article 109403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2025.109403
https://research-portal.uu.nl/ws/files/258849674/1-s2.0-S0378377425001179-main.pdf
van Jaarsveld, B., Wanders, N., Sutanudjaja, E. H., Hoch, J., Droppers, B., Janzing, J., van Beek, R. L. P. H., & Bierkens, M. F. P. (2025). A first attempt to model global hydrology at hyper-resolution. Earth System Dynamics, 16(1), 29-54. https://doi.org/10.5194/esd-16-29-2025
https://research-portal.uu.nl/ws/files/251558930/esd-16-29-2025.pdf
2024
Cuthbert, M. O., Gleeson, T., Bierkens, M. F. P., Ferguson, G., & Taylor, R. G. (2024). Concerns regarding proposed groundwater Earth system boundary. Nature, 635(8039), E4-E5. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-08082-9
https://research-portal.uu.nl/ws/files/247041267/s41586-024-08082-9.pdf
Melo-Leon, S. F., Reinhard, S., Bierkens, M. F. P., & van Beek, R. (2024). HELGA: a global hydro-economic model of groundwater-fed irrigation from a farmer’s perspective. Environmental Research Letters, 19(12), Article 124007. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ad8246
https://research-portal.uu.nl/ws/files/244719728/Melo-Le_n_2024_Environ._Res._Lett._19_124007.pdf
Reinecke, R., Gnann, S., Stein, L., Bierkens, M., de Graaf, I., Gleeson, T., Essink, G. O., Sutanudjaja, E. H., Ruz Vargas, C., Verkaik, J., & Wagener, T. (2024). Uncertainty in model estimates of global groundwater depth. Environmental Research Letters, 19(11), Article 114066. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ad8587
https://research-portal.uu.nl/ws/files/244259726/Reinecke_2024_Environ._Res._Lett._19_114066.pdf
Bierkens, M. F. P. (2024). Foreword. In A. Mukherjee (Ed.), Water Matters: Achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (pp. xvii). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-443-15537-6.00031-8
https://research-portal.uu.nl/ws/files/241655756/3-s2.0-B9780443155376000318-main.pdf
Leijnse, M., Bierkens, M.F.P., Gommans, K., Lin, D., Tait, A., & Wanders, N. (2024). Key drivers and pressures of global water scarcity hotspots. Environmental Research Letters, 19(5), 1-13. Article 054035. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ad3c54
https://dspace.library.uu.nl/bitstream/handle/1874/452258/Leijnse_2024_Environ._Res._Lett._19_054035.pdf?sequence=1
M. F. P., van Beek, R., & Wanders, N. (2024). Gisser-Sánchez revisited: A model of optimal groundwater withdrawal under irrigation including surface–groundwater interaction. Journal of Hydrology, 635, Article 131145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2024.131145 https://dspace.library.uu.nl/bitstream/handle/1874/438410/1-s2.0-S0022169424005407-main.pdf?sequence=1
Verkaik, J., Sutanudjaja, E. H., Oude Essink, G. H. P., Lin, H. X., & Bierkens, M. F. P. (2024). GLOBGM v1.0: A parallel implementation of a 30arcsec PCR-GLOBWB-MODFLOW global-scale groundwater model. Geoscientific Model Development, 17(1), 275-300. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-17-https://dspace.library.uu.nl/bitstream/handle/1874/437695/gmd-17-275-2024.pdf?sequence=1
Zamrsky, D., Oude Essink, G. H. P., & Bierkens, M. F. P. (2024). Global Impact of Sea Level Rise on Coastal Fresh Groundwater Resources. Earth’s Future, 12(1), Article e2023EF003581. https://doi.org/10.1029/2023EF003581 https://dspace.library.uu.nl/bitstream/handle/1874/437096/Earth_s_Future_-_2024_-_Zamrsky_-_Global_Impact_of_Sea_Level_Rise_on_Coastal_Fresh_Groundwater_Resources.pdf?sequence=1
2023
Cuthbert, M. O., Gleeson, T., Bierkens, M. F. P., Ferguson, G., & Taylor, R. G. (2023). Defining Renewable Groundwater Use and Its Relevance to Sustainable Groundwater Management. Water Resources Research, 59(9), Article e2022WR032831. https://doi.org/10.1029/2022WR032831
https://dspace.library.uu.nl/bitstream/handle/1874/438102/Water_Resources_Research_-_2023_-_Cuthbert_-_Defining_Renewable_Groundwater_Use_and_Its_Relevance_to_Sustainable.pdf?sequence=1
Zipper, S., Befus, K. M., Reinecke, R., Zamrsky, D., Gleeson, T., Ruzzante, S., Jordan, K., Compare, K., Kretschmer, D., Cuthbert, M., Castronova, A. M., Wagener, T., & Bierkens, M. F. P. (2023). GroMoPo: A Groundwater Model Portal for Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable (FAIR) Modeling. Groundwater, 61(6), 764-767. https://doi.org/10.1111/gwat.13343
https://dspace.library.uu.nl/bitstream/handle/1874/433301/Groundwater_-_2023_-_Zipper_-_GroMoPo_A_Groundwater_Model_Portal_for_Findable_Accessible_Interoperable_and_Reusable_.pdf?sequence=1